
ALTERATION MODELING
The reaction between hydrothermal solutions and rocks alters the original rock composition leading to form various ore deposits. The pathway of hydrothermal fluids through the crust mark zones of alteration and mineral assemblages, which are significant guides for exploration or exploratory drilling of ore deposits. In order to establish accurate estimations of 3D deposit modeling and mineralization direction, alteration and textural zoning should be thoroughly examined.
Alteration, in simplest form, is the change in mineralogical composition of a rock mass in response to hydrothermal fluid flow that varies as a function of temperature, pressure, host rock composition, fluid composition and the ratio of fluid to rock. The evolution of alteration in a dynamic hydrothermal system is related to initial composition of reaction fluid, pH and temperature with a rock, using constraints imposed by established thermodynamic, chemical and equilibrium data (Reed, 1997).
Hydrothermal alteration processes causing to form clay minerals and further alteration of clay minerals are both decisive, because of the resulting economical ore deposits such as Cu, Zn, Pb, Ag, and Au.
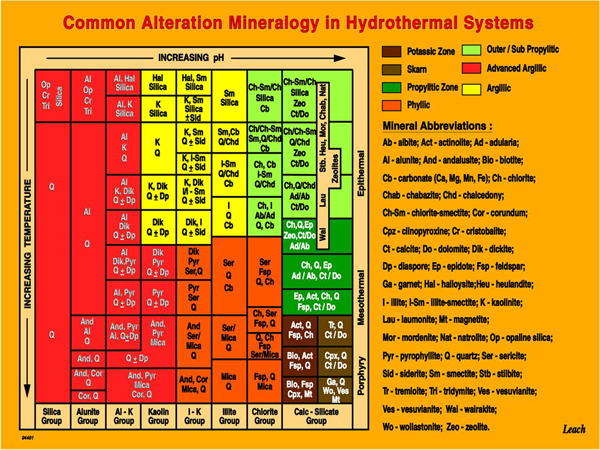
Table 1: Clay alteration under varying pH and temperature conditions (Leach, 1995)
• Potassic alteration is characterized by exchange of K for Ca&Na, leading to replacement of Ca-Na phases by potassic minerals; typical assemblages are orthoclase and biotite after plagioclase and hornblende. It is distinguished commonly in core of porphyry Cu-systems (..).
• Propylitic alteration can be studied in two stages; the epidote stage and the epidote free stage regarding to CO2 pressure conditions. Epidote stage reveals mineral assemblages of epidote-chlorite-sericite, chlorite-sericite and chlorite-epidote-calcite (with or without albite and quartz) whereas epidote free stage assemblages include calcite, chlorite and sericite (Seki, 1973).
• Phyllic alteration is commonly associated with sericite-quartz-pyrite-chlorite assemblages on a wide variety of hydrothermal systems and deposits types such as porphyry, volcanogenic massive sulfide, orogenic and Carlin types (…). It typically forms by the decomposition of feldspars as replacement of feldspars on low pH (acidic) conditions.
• Argillic alteration plays a key role in formation of clay minerals, including kaolinite, smectite and illite. Argillic alteration is generally a low temperature event, and some may occur in atmospheric conditions. The earliest signs of argillic alteration include the bleaching out of feldspars. Advanced argillic alteration, a subcategory of argillic alteration, consists of kaolinite + quartz + hematite + limonite, feldspars leached and altered to sericite. The presence of this assemblage suggests low pH (highly acidic) conditions and temperatures of <220ºC. At higher temperatures, the mineral pyrophyllite (white mica) forms in place of kaolinite.
In geothermal systems textural zones are also important indicators of mineralization characteristics and mineralization-time relations. Thus, cross checking the alteration patterns with textural zoning provide a better understanding of fluid evolution and ore formation. The cases of gold exploration in epithermal systems, mineralization is primarily distinguished between high and low sulphidation which evolve through differing fluid paths (Corbett and Leach, 1998). Distinction between varying styles of epithermal gold mineralization is identified from ore and gangue mineralogy, some styles display supergene enrichment (quartz-sulphide gold + copper) (Corbett, 2002). The residual silica a product of silicification forms different silica types with significant zonation.
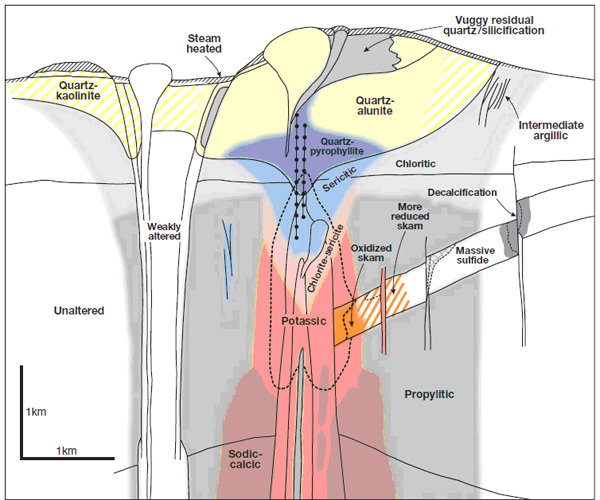
Figure 1: Conceptual modeling of hydrothermal alteration which related to porphyry and epithermal mineralization (Sillitoe,2010).
In conclusion, identification of alteration patterns and textures provide valuable information to interpret the nature of the hydrothermal system, ore formation and predict the changes occurred in the past. Therefore, with the inside of alteration modeling vital exploration issues like exploratory drilling, mining technique and direction estimations could be done economically.